Source and more : Nature.com Science Reports
Abstract
Changes in the Earth’s water cycle can be estimated by analyzing sea surface salinity. This variable reflects the balance between precipitation and evaporation over the ocean, since the upper layers of the ocean are the most sensitive to atmosphere–ocean interactions.
In situ measurements lack spatial and temporal synopticity and are typically acquired at few meters below the surface.
Satellite measurements, on the contrary, are synoptic, repetitive and acquired at the surface. Here we show that the satellite-derived sea surface salinity measurements evidence an intensification of the water cycle (the freshest waters become fresher and vice-versa) which is not observed at the in-situ near-surface salinity measurements. The largest positive differences between surface and near-surface salinity trends are located over regions characterized by a decrease in the mixed layer depth and the sea surface wind speed, and an increase in sea surface temperature, which is consistent with an increased stratification of the water column due to global warming.
These results highlight the crucial importance of using satellites to unveil critical changes on ocean–atmosphere fluxes.
…… / ……
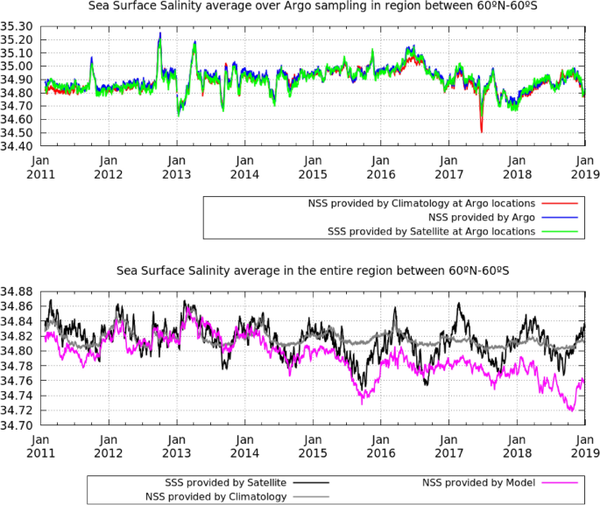
From: Increasing stratification as observed by satellite sea surface salinity measurements
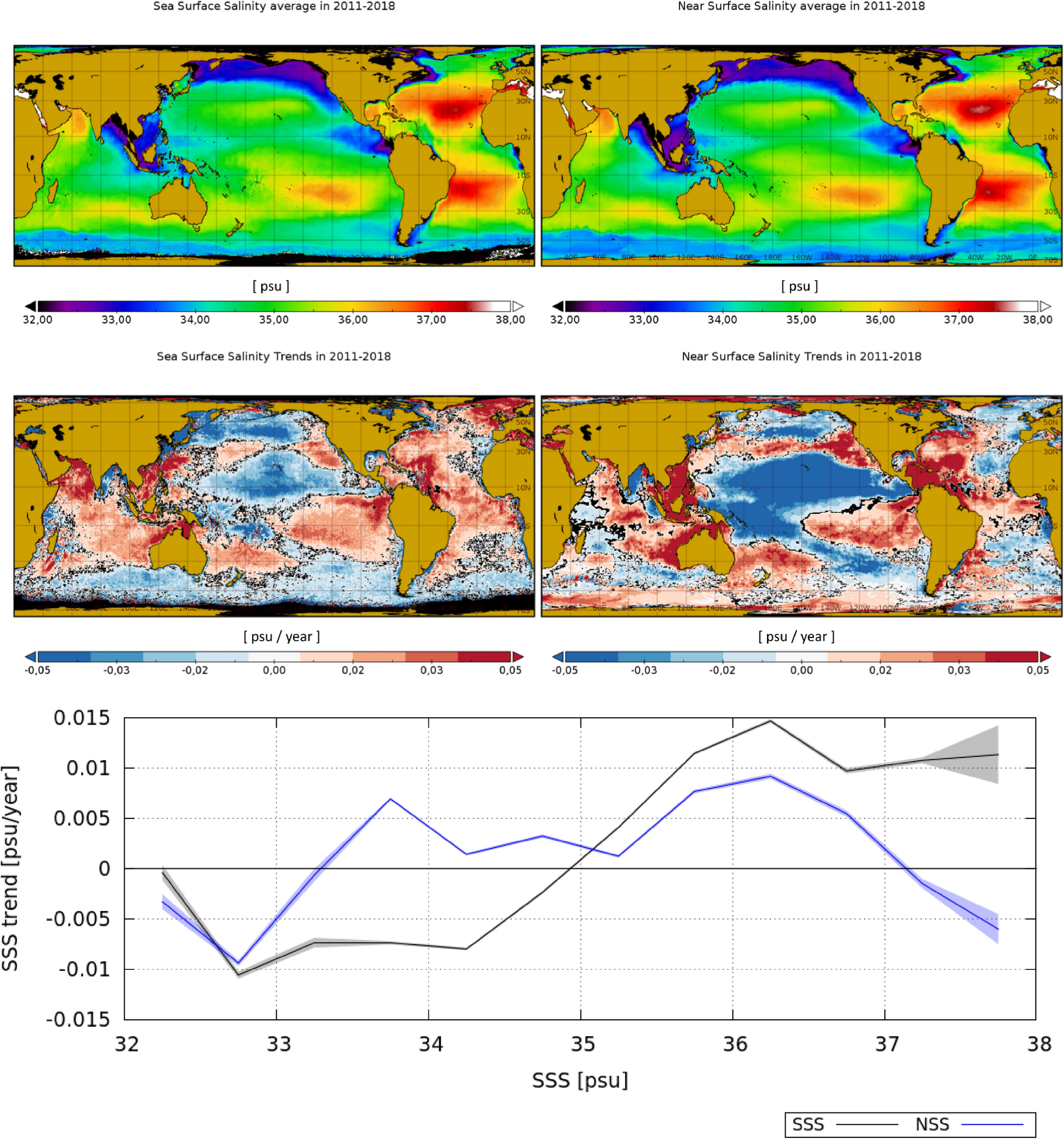
Top row: salinity average in 2011–2018 as observed by the satellite (SSS) (left) and by the model (NSS) (right). Middle row: satellite SSS trends (left) and model NSS trends (right) in 2011–2018. Locations with trends being different from zero with a 95%95% level of confidence are represented in black. Bottom plot: mean SSS (black) and NSS (blue) trend as a function of averaged SSS and NSS (respectively) in the same period. The shadowed area represents the confidence interval of the 95%95%. Maps are plotted with Panoply v 4.12.0 (https://www.giss.nasa.gov/tools/panoply/).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-10265-1
Read also :
https://www.sciencealert.com/earth-s-water-cycle-is-accelerating-and-it-s-cause-for-great-concern